Table of Contents
Jaw cancer surgery, also known as mandibular cancer surgery is performed for Jaw (mandibular) cancer, is a type of oral cancer that affects the jawbone. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including tobacco use, alcohol consumption, and exposure to certain chemicals or radiation. Surgery is a common treatment for jaw cancer, and it involves removing the cancerous tissue and any nearby lymph nodes. In this article, we will provide an in-depth look at jaw cancer surgery, including the indications for the procedure, the procedure itself, recovery, risks, and benefits.
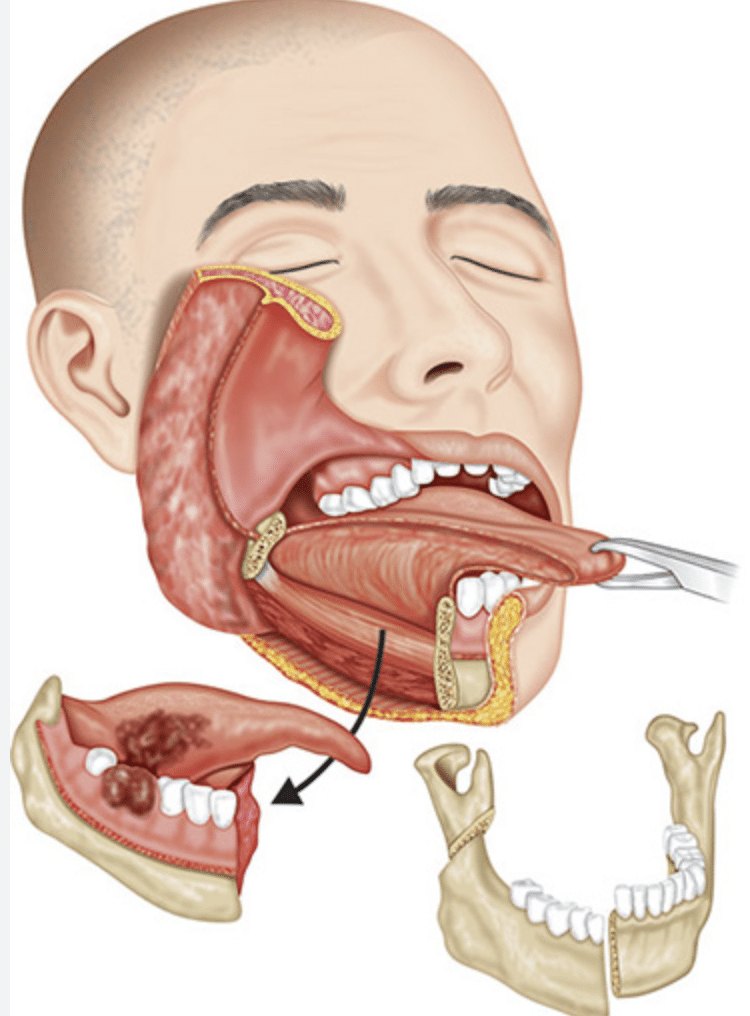
Indications for Jaw Cancer Surgery:
The most common indication for jaw cancer surgery is the presence of a tumor in the jawbone that has been confirmed as cancerous. In some cases, surgery may be recommended even if the tumor is not cancerous, but it is causing pain or discomfort, or if there is concern that it could develop into cancer in the future. Additionally, if the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes, surgery may be necessary to remove the affected lymph nodes.
Procedure:
Jaw cancer surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia, which means that the patient is asleep during the procedure. The procedure involves making an incision in the jaw to gain access to the tumor. The tumor and any affected tissue or lymph nodes are carefully dissected and removed from the surrounding tissue. The incision is then closed with sutures or staples.
In some cases, if the tumor is large or located close to important structures such as nerves or blood vessels, the surgeon may use a more complex technique such as reconstructive surgery to restore the appearance and function of the affected area.
Recovery:
After the procedure, the patient will be monitored in the recovery room until they are fully awake and stable. Most patients will need to stay in the hospital for a few days for observation and to manage pain and other symptoms. After leaving the hospital, patients will need to follow a strict regimen of oral care to promote healing and reduce the risk of infection.
Recovery time varies, but most people can return to normal activities within a few weeks after the procedure. Common side effects after surgery include pain, swelling, and bruising in the affected area. Pain can typically be managed with over-the-counter pain medication or prescription pain medication if necessary.
Risks:
As with any surgery, jaw cancer surgery carries some risks, such as bleeding, infection, and complications related to anesthesia. Bleeding is the most common complication, and it can occur up to two weeks after the surgery. In some cases, bleeding may require a return trip to the operating room.
Infection is another potential risk of jaw cancer surgery. Antibiotics may be prescribed after the surgery to reduce the risk of infection. Complications related to anesthesia, such as a reaction to the medication, are rare but can occur.
Benefits:
Jaw cancer surgery has several benefits, particularly in cases where the tumor is causing pain or discomfort, or if there is concern that it could develop into a more serious condition. Removing the tumor can also improve the appearance of the affected area and restore normal function, such as the ability to speak or eat.
Additionally, if the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes, removing the affected lymph nodes can help to prevent the cancer from spreading further and improve the chances of a positive outcome.
Conclusion:
Jaw cancer surgery is a common surgical procedure that is typically performed to remove cancerous tumors in the jawbone or nearby lymph nodes. While there are risks associated with the procedure, the benefits of jaw cancer surgery can be significant, particularly in cases where the tumor is causing pain or discomfort or if there is concern that it could develop into a more serious condition. If you are considering jaw cancer surgery, it is important to discuss the risks and benefits of the procedure with your healthcare provider, and to consider the potential costs.
Reconstruction for Jaw Cancer Surgery
Reconstruction following jaw (mandibular) cancer surgery is a critical step in restoring both the appearance and function of the affected area. Depending on the extent of the cancer and the amount of tissue that needs to be removed, reconstruction may involve a variety of techniques to rebuild the jaw and surrounding structures.
Here are some common techniques used in reconstruction after jaw cancer surgery:
Free Flap Reconstruction: This technique involves removing healthy tissue from another part of the body, such as the thigh or abdomen, and transplanting it to the jaw area to rebuild the missing tissue. Blood vessels from the transplanted tissue are then attached to blood vessels in the jaw area to provide a new blood supply.
Pedicled Flap Reconstruction: This technique involves taking healthy tissue from a nearby area, such as the neck or chest, and using it to reconstruct the missing tissue in the jaw area. Unlike free flap reconstruction, the tissue remains attached to its original blood supply.
Bone Grafts: In some cases, bone tissue may need to be removed during jaw cancer surgery. Bone grafts can be used to rebuild the missing bone and provide support for the surrounding tissue. The graft may be taken from another part of the body or from a donor.
Dental Implants: After reconstruction, dental implants can be used to replace missing teeth and restore normal chewing and speaking abilities.
The specific technique used in reconstruction after jaw cancer surgery will depend on the individual patient’s needs and the extent of the cancer. Reconstruction may be performed immediately after the cancer surgery or in a staged approach over several procedures.
Reconstruction after jaw cancer surgery is typically performed by a team of healthcare providers, including a surgeon, a plastic surgeon, and a prosthodontist. Patients may need to stay in the hospital for several days after reconstruction to monitor for any complications or to manage pain and other symptoms.
In conclusion, reconstruction after jaw cancer surgery is a critical step in restoring both the appearance and function of the affected area. The specific technique used in reconstruction will depend on the individual patient’s needs and the extent of the cancer. Patients should discuss the potential risks and benefits of reconstruction with their healthcare provider to determine if it is right for them.
Adjuvant therapy is a type of treatment that is used after surgery to remove jaw (mandibular) cancer to help reduce the risk of the cancer returning or spreading to other parts of the body. Adjuvant therapy can include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of both. The specific type of adjuvant therapy recommended will depend on the individual patient’s needs and the extent of the cancer.
Radiation Therapy:
Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy may be recommended after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells in the area of the jaw where the tumor was removed. Radiation therapy may also be recommended if the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes or other areas of the body.
Radiation therapy is typically administered over a period of several weeks, with daily treatments that last only a few minutes each. Side effects of radiation therapy may include fatigue, skin irritation, and dry mouth.
Chemotherapy:
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy may be recommended after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells in the area of the jaw where the tumor was removed. Chemotherapy may also be recommended if the cancer has spread to other areas of the body.
Chemotherapy is typically administered in cycles over several months, with breaks in between to allow the body to recover. Side effects of chemotherapy may include nausea, fatigue, and hair loss.
Combination Therapy:
Combination therapy, which includes both radiation therapy and chemotherapy, may be recommended in some cases to provide a more comprehensive approach to treating jaw cancer. Combination therapy may be particularly effective in cases where the cancer has spread to other areas of the body.
The decision to undergo adjuvant therapy will depend on the individual patient’s needs and the extent of the cancer. Patients should discuss the potential risks and benefits of adjuvant therapy with their healthcare provider to determine if it is right for them.
It is important for patients to follow up with their healthcare provider regularly after adjuvant therapy to monitor for any potential side effects or recurrence of the cancer. Adjuvant therapy can help to improve the chances of a positive outcome after jaw cancer surgery, and it can help to reduce the risk of the cancer returning or spreading to other parts of the body.
Jaw (Mandibular) Cancer Surgery Cost
The cost of jaw (mandibular) cancer surgery can vary depending on several factors, including the location of the treatment facility, the experience of the healthcare provider, the extent of the surgery required, and any additional treatments or procedures that may be necessary. In addition, the cost of jaw cancer surgery may also include other expenses such as hospital stays, anesthesia, imaging tests, and follow-up care.
In the United States, the cost of jaw cancer surgery can range from $10,000 to $30,000 or more, depending on the specific procedure and location. The cost of the surgery may be covered by health insurance, but this will depend on the individual patient’s insurance plan and coverage.
In other countries such as India, the cost of jaw cancer surgery may be much lower, ranging from $2,500 to $8,000 or more, depending on the location and specific procedure required. However, patients should be aware that traveling abroad for medical treatment can involve additional expenses such as travel costs, lodging, and meals.
In some cases, financial assistance may be available to help offset the cost of jaw cancer surgery. Patients should check with their healthcare provider or hospital to see if they offer any financial assistance programs, or if there are any nonprofit organizations that can provide financial support.
Ultimately, the cost of jaw cancer surgery will depend on several factors, and it is important for patients to discuss the potential costs with their healthcare provider and insurance company to understand their options and make an informed decision about their treatment.
Jaw Cancer Surgery Cost in Turkey
The cost of jaw (mandibular) cancer surgery in Turkey can vary depending on several factors, such as the location of the treatment facility, the extent of the surgery required, the experience of the healthcare provider, and any additional treatments or procedures that may be necessary. In general, healthcare services in Turkey are known to be of high quality and relatively affordable compared to other countries.
The cost of jaw cancer surgery in Turkey can range from $15,000 to $40,000 or more, depending on the specific procedure and location. However, patients should be aware that the cost of surgery may also include additional expenses such as hospital stays, anesthesia, imaging tests, and follow-up care.
In some cases, medical tourism companies may offer package deals that include transportation, lodging, and other expenses related to medical treatment in Turkey. However, patients should be cautious when considering medical tourism and should thoroughly research any companies or facilities before committing to treatment.
Patients should also check with their insurance provider to determine if the cost of jaw cancer surgery in Turkey will be covered under their insurance plan. Some insurance plans may require prior authorization or may only cover a portion of the cost of treatment.
In conclusion, the cost of jaw cancer surgery in Turkey can be relatively affordable compared to other countries, but it is important for patients to research their options and understand the potential costs and risks associated with treatment. Patients should also work closely with their healthcare provider and insurance company to ensure that they receive the best possible care at a cost that is reasonable and affordable for them.
